Hadoop(四)TF-IDF 算法原理与实现
原理
『TF-IDF』是一种用于资讯检索与资讯探勘的常用加权技术。
主要思想是:如果某个词或短语在一篇文章中出现的频率高,并且在其他文章中很少出现,则认为此词或者短语具有很好的类别区分能力,适合用来分类。
『TF-IDF』实际上是:『TF』(词频) * 『IDF』(逆向文件频率)。『TF』指的是某一个给定的词语在一份给定的文件中出现的次数。这个数字通常会被归一化(分子一般小于分母,区别与『IDF』),以防止它偏向长的文件(同一个词语在长文件里可能会比短文件有更高的词频,而不管该词语重要与否);『IDF』是一个词语普遍重要性的度量。某一特定词语的『IDF』,可以由总文件数目除以包含该词语之文件的数目,再将得到的商取对数得到。
TF公式:
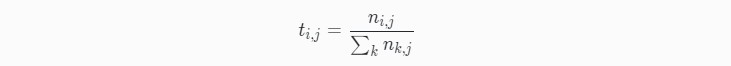
n_{i,j} 是该词在文件 $d_j$ 中的出现次数;而分母则是在文件 $d_j$ 中所有字词的出现次数之和。
IDF公式:

即:
$$ idf = log (语料中文件的总数 / 包含词语 t 的文件数目) $$
$\mid$ D $\mid$ 是语料库中的文件总数;$\mid$ {j:$t_i$ $\in$ $d_j$} $\mid$ 包含 $t_i$ 文件的数目。如果该词语不在语料库中,就会导致被除数为零,因此一般情况下使用 1 + $\mid$ {j:$t_i$ $\in$ $d_j$} $\mid$ 。
TF-IDF公式:
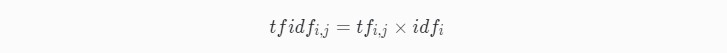
某一特定文件内的高词语频率,以及该词语在整个文件集合重的低文件频率,可以产生出高权重的『TF-IDF』。因此,『TF-IDF』倾向于过滤掉常见的词语,保留重要的词语。
实现
- 分词
- 面向文本计算词频
- 面向全量文本计算包含集合
- 套用公式


第一次:词频统计+文本总数统计
FirstMapper.java
public class FirstMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 按行读取并以制表符分割
String[] v = value.toString().trim().split("\t");
if (v.length >= 2) {
String id = v[0].trim();
String content = v[1].trim();
StringReader sr = new StringReader(content);
// 进行字符串的分词操作
IKSegmenter ikSegmenter = new IKSegmenter(sr, true);
Lexeme word = null;
while ((word = ikSegmenter.next()) != null) {
String w = word.getLexemeText();
// 生成新的key //今天_3823890210294392 1
context.write(new Text(w + "_" + id), new IntWritable(1));
}
context.write(new Text("count"), new IntWritable(1));
} else {
System.out.println(value.toString() + "************");
}
}
}
FirstReduce.java
public class FirstReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> iterable,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
// 相同的key循环迭代
for (IntWritable i : iterable) {
sum = sum + i.get();
}
if (key.equals(new Text("count"))) {
System.out.println(key.toString() + "*********** " + sum);
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
第二次:字词集合统计:逆向文件频率
TwoMapper.java
public class TwoMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 获取当前 mapper task的数据片段(split)
FileSplit fs = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
if (!fs.getPath().getName().contains("part-r-00003")) {
String[] v = value.toString().trim().split("\t");
if (v.length >= 2) {
String[] ss = v[0].split("_");
if (ss.length >= 2) {
String w = ss[0];
// 形成新的key
context.write(new Text(w), new IntWritable(1));
}
} else {
System.out.println(value.toString() + "*************");
}
}
}
}
TwoReduce.java
public class TwoReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> arg1, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable i : arg1) {
sum = sum + i.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
第三次:取1、2次结果最终计算出字词的TF-IDF
LastMapper.java
public class LastMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> {
// 存放微博总数
public static Map<String, Integer> cmap = null;
// 存放df
public static Map<String, Integer> df = null;
// 在map方法执行之前
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
if (cmap == null || cmap.size() == 0 || df == null || df.size() == 0) {
Path[] ss = context.getLocalCacheFiles();
if (ss != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
Path uri = ss[i];
if (uri.toUri().getPath().endsWith("part-r-00003")) {// 微博总数
Path path = new Path(uri.toUri().getPath());
try {
// 从缓存中读取
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(uri.toUri().getPath()));
String line = br.readLine();
if (line.startsWith("count")) {
String[] ls = line.split("\t");
cmap = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
cmap.put(ls[0], Integer.parseInt(ls[1].trim()));
}
br.close();
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}
} else if (uri.toUri().getPath().endsWith("part-r-00000")) {// 词条的DF
df = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(uri.toUri().getPath()));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] ls = line.split("\t");
df.put(ls[0], Integer.parseInt(ls[1].trim()));
}
br.close();
}
}
}
}
}
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
FileSplit fs = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
if (!fs.getPath().getName().contains("part-r-00003")) {
String[] v = value.toString().trim().split("\t");
if (v.length >= 2) {
int tf = Integer.parseInt(v[1].trim());// tf值
String[] ss = v[0].split("_");
if (ss.length >= 2) {
String w = ss[0];
String id = ss[1];
double s = tf * Math.log(cmap.get("count") / df.get(w));
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getInstance();
nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(5);
context.write(new Text(id), new Text(w + ":" + nf.format(s)));
}
} else {
System.out.println(value.toString() + "***************");
}
}
}
}
LastReduce.java
public class LastReduce extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> iterable, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (Text i : iterable) {
sb.append(i.toString() + "\t");
}
context.write(key, new Text(sb.toString()));
}
}
最终结果如下:

本文由 caroly 创作,如果您觉得本文不错,请随意赞赏
采用 知识共享署名4.0 国际许可协议进行许可
本站文章除注明转载 / 出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名
原文链接:https://caroly.fun/archives/tf-idf算法原理与实现
最后更新:2021-05-15 20:45:26